When my husband and I bought our 35 acres in the Rocky Mountains of Colorado, it felt like a dream. Mountain vistas, driving distance to ski mountains, and unbroken views of the most pristine high-altitude wildflower valleys. But those unbroken views came with a price: we were ten miles away from any power lines to tap into to get power to our future home. That’s when I fell down the rabbit hole of off-grid power sources.
Contents
For anyone that lives in the city or suburbs (which was me not too long ago!), we take for granted the capability to have electricity whenever we want it. Flip a switch, and on it goes. It isn’t until snow storms, earthquakes, hurricanes, and tornadoes impact the power grid that we suddenly realize how fragile our access to electricity can be.
Prepare today for peace of mind tomorrow.
Get occasional tips about keeping your family and home safe — delivered to your inbox.
Why Everyone Should Have Back-Up Off-Grid Power Sources
Even if you aren’t looking to live off-grid, having a backup energy source can be a very helpful tool. Should a natural disaster hit, an unexpected emergency occurs at the city power plant, or even a utility cyberattack, your backup power source could mean the difference between having heat running in the winter or the A/C keeping you cool in the summer.
Typically, areas that are prone to winter storms and hurricanes promote the use of generators to survive several days without power (which can be common after a major storm event). These generators predominantly rely on gasoline or propane, though more solar generator options are now available on the market than even a few years ago.
These can be great tools in the face of natural disaster threats. But what about threats such as rolling blackouts or utility cyberattacks?
In situations such as these, which may not come with a weather forecast warning, you may not have time to refill your gas and propane tanks to run your generator. Similarly, you may not have enough fuel if the power is out for a week or more. While the likelihood is low that your power will be out for that long, being prepared to survive and thrive during an occurrence like that is a fantastic reason to invest in backup off-grid power sources.
How to Get Power Off-Grid
When it comes to off-grid power options, there are actually many selections depending on how you want to draw your power: solar, wind, water, and geothermal energy are a few renewable energy sources. Depending on what kind of home you live in, where you live in the world, and what kind of investment you are willing to make will all determine which solution makes the most sense for you.
Solar Panels
Arguably the most well-known form of renewable energy, solar power was once something out of science fiction novels. Now, in some parts of the country, you can see entire neighborhoods with panels on the roofs of houses. Some counties and states are even drafting legislation that requires new buildings and commercial infrastructure to use solar panels.
While we won’t go into the engineering specifics of how solar panels actually convert the sun’s rays into energy, or how to install a solar array on your roof, we can discuss the pros and cons of this type of system. The pros are that if you live in the South or Western parts of the country, the sun is often in ample supply. Harnessing the sun’s energy to power your house full-time or as a backup source is a good choice for these areas. Even in parts of New England, I’ve followed bloggers who remain grid-tied but installed supplementary solar power systems.
They’re able to generate electricity at a rate that is higher than they’ll use in the summer, pumping power back to their electric utility. In some cases, they’ll actually get paid to produce energy. Generating electricity through their solar panels ends up being a small source of income, even if only in the summer months!
Some cons include higher upfront costs to purchase the components and have them installed. You’ll need space for panels that aren’t blocked by other buildings or trees. Or be on the fringe and have solar roof tiles installed so that they blend into your roof line. Solar roof tiles actually take the place of asphalt tiles or metal roofing but convert the sun’s rays into electricity.
You’ll also need a place indoors to store the other components of a system, such as the battery bank and inverters.
It’s also important to note that solar panels alone won’t be helpful if the electrical grid is impacted. In that case, you’ll need a full solar system, complete with batteries to collect the sun’s energy to use overnight.
Adopting off-grid power technologies represents a proactive approach to preparedness, offering a buffer against the vulnerabilities of centralized power systems. As natural disasters continue to impact millions globally, the importance of having a reliable and renewable energy source cannot be overstated. Whether through solar panels, wind turbines, or hydroelectric power, these systems not only provide energy security but also contribute to environmental sustainability, aligning with the broader goals of reducing carbon footprints and promoting renewable energy use.
– Eddie Penney Emergency Prep Expert
Use a battery bank to store electric energy
Avoiding the complexities of how solar systems work, at the most basic level, it’s important to understand that solar panels don’t hold on to the energy they convert from the sun’s rays. They capture it and that power can be used automatically. But if you want electric power on a cloudy day or overnight, when the sun isn’t visible, you’ll need a battery bank.
This is when the cost of installing a solar system can increase tremendously. A full system will include solar panels, batteries, inverters, wires, cables, conduits, circuit breakers, combiner boxes, and more.
It may sound complicated, but there are many reputable companies that can help you to install a solar power system, even if you remain grid-tied. The important thing to remember is that without battery storage, you won’t have any power overnight. So if the weather is cold or hot where you live, it will be that much more difficult to maintain the temperature in your home while the sun is hidden beyond the horizon.
Windmills and Wind Turbines
Another well-known choice for off-grid energy is wind power. If you live in an area with average wind speeds of 10–20 miles per hour, you could take advantage of wind power as a backup energy source.
Why don’t more people utilize wind power? One of the cons of using a wind turbine is that to generate enough power, turbines normally have to be very large. That’s one reason why when you drive through the middle of the U.S., you see hundreds of huge turbines spinning across the landscape. However, using wind as an alternate or supplemental source of power, particularly if you do live in a windy area, could be an option.
Whether you remain grid-tied and want a backup method or are considering a full off-grid shift, there are pros to using wind power as well. Wind turbines for residential use are much smaller than the gargantuan machines described above.
If you live in the plains, in the mountains, or along the coasts, you’re likely in an area that could use a wind turbine for off-grid energy generation. When it comes to commercial wind power, large, flat areas where many, many wind turbines can be installed are currently leading in electrical output:
The five states with the most electricity generation from wind in 2021 were Texas, Iowa, Oklahoma, Kansas, and Illinois. These states combined produced about 56% of total U.S. wind electricity generation in 2021.^2
Other cons include wind electric systems needing to be professionally installed, finding the right site and having enough room for them, and upfront costs. Some costs could be mitigated with federal tax credits and other programs, as well as state options.
A strong off-grid power system would combine solar and wind power (a hybrid system) to fully power an off-grid home, without leaving yourself vulnerable to the availability of solar or wind alone. The combination of a small solar system supplemented by a wind turbine could easily bring in enough power for a rural farm that is too far from utility suppliers, giving you energy independence. But even for grid-tied city dwellers, even the smallest wind turbines could supply a small trickle of energy when your main source goes down.
To learn more, visit the U.S. Department of Energy’s page on small wind electric systems.
Hydroelectric Power
If you’re lucky enough to live close enough to running water to create your own off-grid hydroelectric system, first of all, let me say “congratulations” to you because that sounds magical.
Hydroelectric power is the process of using running water to generate electricity. Dams and old-fashioned water wheels are two forms of hydroelectric power systems. While water wheels are low-tech, with enough water, they are excellent options for generating power. It’s why over 2,000 dams are used across the U.S. to produce electricity for millions of homes.
Now, hydroelectric power is clearly not for every household. If you rent an apartment in the midst of suburban sprawl with nary a river in sight, then no, this is not for you. However, for any homes that have access to a river or stream consistently through the year, you could invest in a microhydro electricity/power system^3.
By using water power, the force of the running water could power a turbine, creating electricity (an oversimplification but it’s the general concept). These micro-hydroelectric systems could be a DIY project, depending on your comfort with engineering, electricity, and willingness to learn. But you could also work with a local engineer to have a system installed.
While not right for many people, micro-hydro electrical systems can have high energy efficiency, making it a worthwhile off-grid investment for some.
Biogas/Biopower Generator
If you thought that hydroelectric energy systems were a bit quirky, do I have an even stranger system for you. Meet the biomass generator.
Biogas systems use agricultural by-products, human sewage, and discarded food to create an enclosed compost system. Within this system, bacteria are added to induce natural microorganism interactions. When these interactions occur, they break down biological products and convert them into gases. These clean, energy-efficient gases are then channeled through pipes that can be connected to stoves, water heaters, and more.
If it sounds a little bit like magic, you’re not wrong. It’s essentially capturing natural decomposition cycles, speeding them up, and then utilizing the byproducts to make dinner or take a hot shower.
If you don’t have any other choice than to live off-grid or are interested in going off-grid, this is a very interesting option. There are several small companies that are creating residential biogas systems that can provide power to an entire home. As a backup off-grid power system, there is certainly potential. If you have space in your backyard, these systems almost work like composters. If you already compost, you could put your food scraps into a biogas system and work on building a backup energy reserve.
The main pull for these systems is often energy conservation. However, they require very little maintenance, and if you’re worried about your impact on the environment and want another energy source, this could be the right fit for you.
What About Generators?
If your level of investment is low, but you are still concerned about having a backup off-grid energy source that can produce electricity, a generator is still a solid option. While a gas generator is a solid option that is easy to find, you’re reliant on having enough gasoline or diesel fuel to power them. If you choose a generator that is powered by a solar panel, then you only need access to unblocked sunshine to keep your generator running.
Whether you choose one of our gas generator options or solar generator options, both are great choices for backup off-grid power systems. Most people who live fully off-grid have some form of generator in case their solar or hybrid system fails.
Honda: Portable Generator

WHY WE RECOMMEND IT
- It’s versatile and user-friendly.
- Has an app that allows users to control the generator from their phone.
- It continuously monitors carbon monoxide (CO) levels.
- The very quiet (~48 decibels) operating noise level.
BEST FOR
- People with small homes and those who need power on the go.
Geneverse Solar Generator
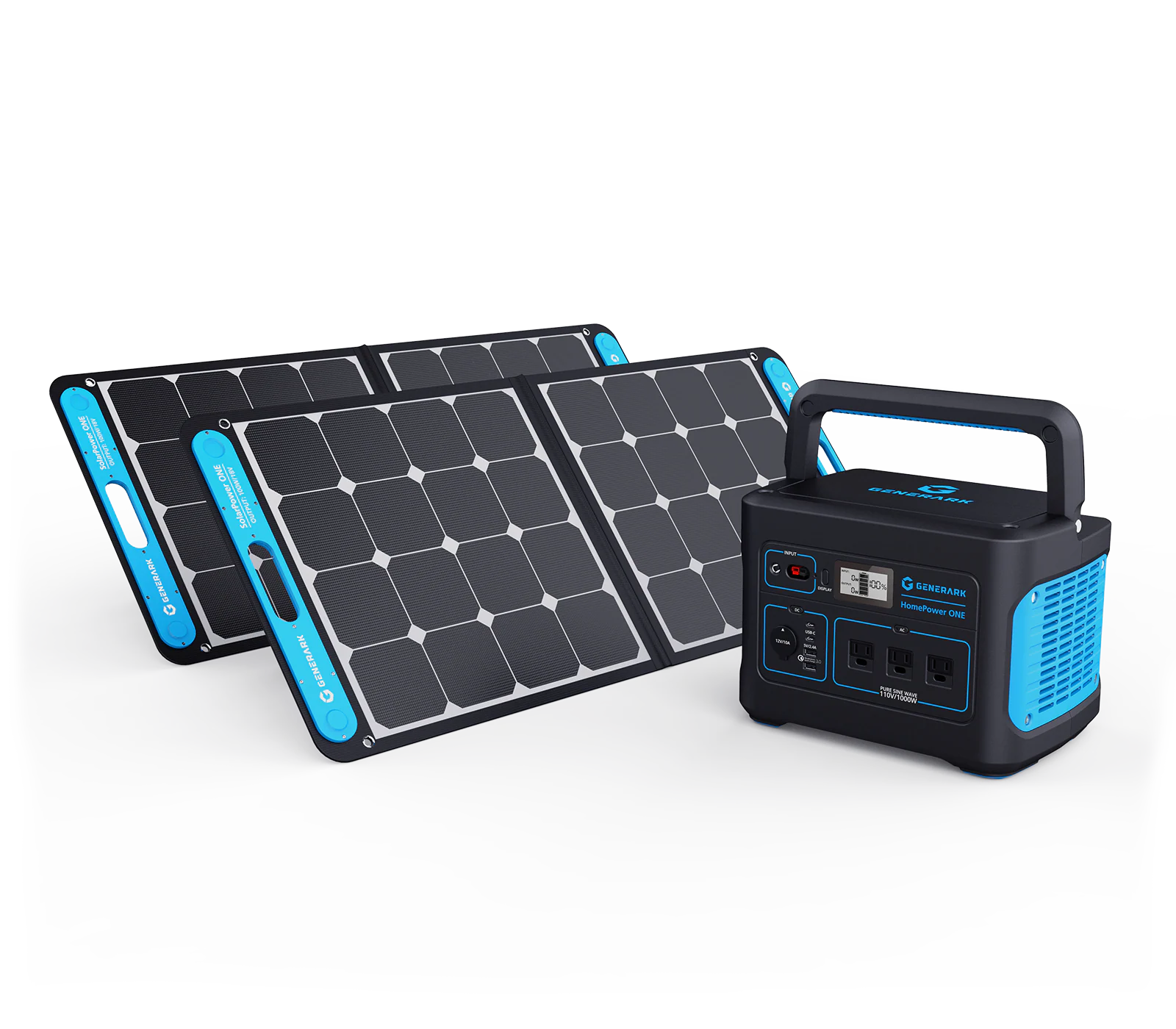

WHY WE RECOMMEND IT
- It has a continual emergency power supply for charging devices and running home appliances.
- It’s quiet and safe for indoor use.
- It can be charged with solar power, an AC outlet, or from your vehicle.
BEST FOR
- Those wanting to be environmentally conscious.
- Residents of states with a high percentage of annual sunny days.
Generac 8000 Watt Generator

WHAT WE LOVED
- This generator will automatically start when electricity is lost, and provide sufficient wattage to power your entire home.
- It’s commercial-grade quality.
- It’s portable.
BEST FOR
- Homeowners.
Getting Started With Getting Off-Grid Power
If all of this feels overwhelming, and you aren’t sure what you actually need to be prepared for extended power outages or surviving natural disasters, read through our archives of expert tips. You can access these at any time at Batten’s Resources blog. You can also view all our expert-vetted, highly recommended power generation solutions in our Marketplace.
Sources:
- U.S. Department of Energy
- U.S. Energy Information Administration
- U.S. Department of Energy